
Data that should be taken from ERP for planning;
A series of operations and machines are linked in the work plan. This sequence may also contain alternative stations and conditional loops. The actual plan of the production unit (selected alternative station) is not determined until the finest planning stage of the order. The work plan is defined for each product and applies to its variants. It can be raw materials or pre-products. Pre-products produced internally are also matched in MES.
In planning, the sequence number is clearly identified in a business plan by means of a sequence number (sequence number 100, 200, 300 etc.). It is used in many systems and allows alternative or parallel working sequences to be easily integrated into the numerical scheme.
The operation defines what is done during the production phase and all the resources allocated (how the production step is executed). The operations are either defined prior to the creation of the work plan or can be created during compilation of the work plan.
Business center / workstation. When a machine is linked with an automatic or manual workstation, it indicates the stage of production. Operations can alternatively be performed on several machines (machine A or machine B as an emergency strategy) or in parallel on several machines (eg both machine A and machine B to increase capacity). These alternative or parallel stations are specially marked in the work plan. The corresponding alternative or parallel machine can be selected in the operations planning system or during execution.
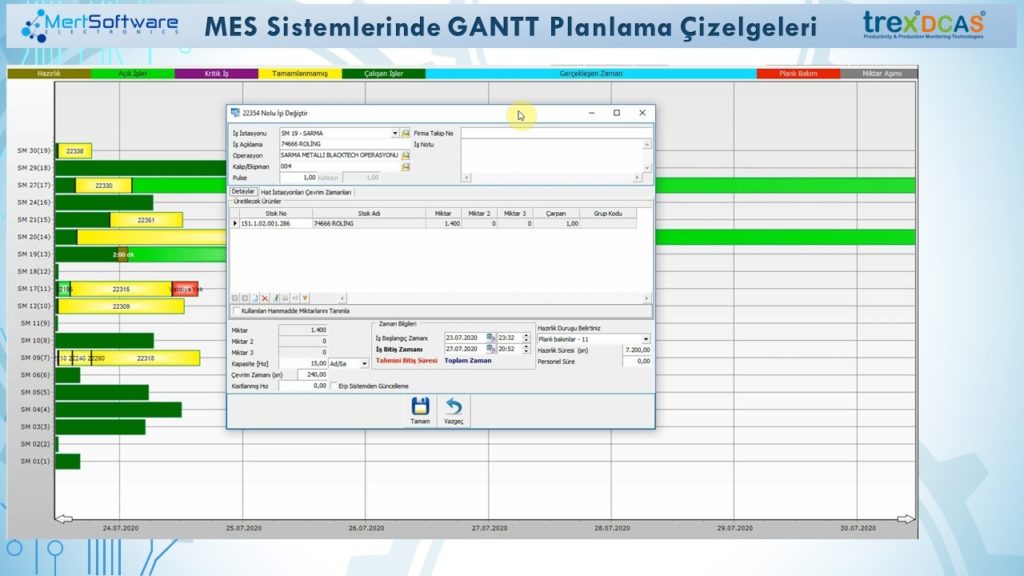
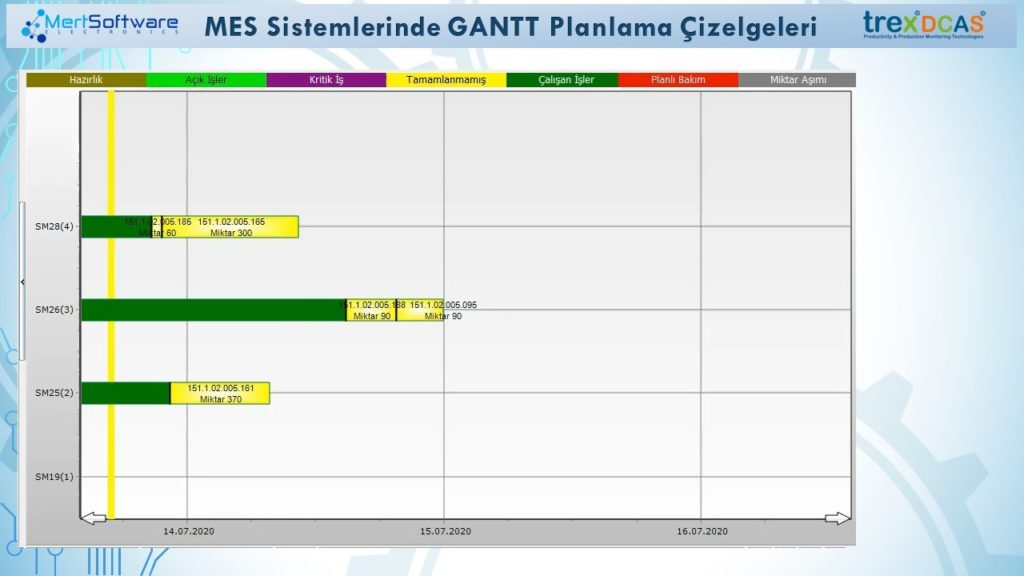
Production intervals and sequences can be displayed in the chart, the period between the earliest possible production start and the end of the last process can be traced.
With MES, being able to monitor all business plans, the history of the work done, the things to be done, the costs and the efficiency of all the assests owned as a result, allows the businesses to manage its equipment correctly. It can be seen how long a equipment has completed its life, whether periodic maintenance time come or not.
Unnecessary purchases can be prevented by instantly accessing the quantity, status and location information of the available equipment.
All work centers involved in a particular production process can be compared with each other and optimized. For this analysis, a database containing detailed information about each production order step is presented to the user. Various criteria such as preparation time, time worked, machine capacity, quality rate can be used to compare relevant work centers. It is also possible to display the capacity usage. This feature informs the user, when and how much of which resources are used in relevant production order. Capacity Management also provides data on which operator will work in which operation, personnel capacity status and whether another planning can be made efor idle capacities in relation to personnel capacities.
A planner needs a lot of information in order to make an accurate and effective planning. These are the work order information opened in line with the specifications and quantity of the ordered product.
MES has the opportunity to look at the features of all orders collectively. Also a lot of information about production work orders, such as starting and ending times, waiting times, work flow times and transit times between work centers, as well as delays in operation can be displayed. Capacity planning (which can be called the most important part ) is based on the business center’s calender or the factory calendar.
The calculation is based on detailed information about stoppage times, exception days and shifts. Beside of these, information about production relations and scheduling rules can also be obtained from the system. Thus, linked production orders can be observed, activities can be compared and different schedules can be analyzed.
The capacity of worstations under influence of three factors :
The essential factors for us in capacity distribution are product variety and production time.
Planning has a close interaction with production management, material requirement planning, maintenance management, quality management and route management modules. It can also be integrated with advanced planning, scheduling and supply chain optimization solutions.
Supply Chain
Supply chain processes that companies have to manage have five critical dimensions consisting of supply, stock, production, inventory and storage.
Achieving these solutions, which are described as “hidden opportunities” and will provide total cost savings of 5-15%, is almost impossible without using an MES.
– Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Most of businesses use MRP Systems to reduce operating costs and to develop effectively. An effective planning, correct data, management support and user knowledge are required for an MRP system to be successful. We can discuss an MRP System under 4 main headings and see the added value of MES.
Growing in Turkey, which has an OEE average of 50%, is a bit difficult. While successive and endless machine leases create additional investments, the needs for a new physical areas and the employment of operators who will use these machines and etc. expenses become imperative. MES has a decisive role in machinery and equipment investments. It would be better to examine this in two areas.
The first is the right equipment selection. For example, you need a laser machine, you have determined it, but what features should it have, how should its driver be, which machine features adapt to your processes in set-up processes? What kind of additional features should there be on the machine to ensure process fluidity in inter-operational layout? What critical stocks should be kept in machine parts?
Second, how much of the existing capacity is being used should be determined. After that, our machine needs should be clarified. Instead of adding a new one to the machines that we cannot use efficiently, we should measure our usability and invest in the right number of machines. A company that has minimized their unplanned downtime can carry out the process by purchasing 2 laser machines instead of 3 for a new project investment, but the other company that does not know this because it can not measure, unfortunately, has invested in an extra laser machine.